Neuroblastoma is a cancer that begins from the nerve cells found in numerous parts of the body. Neuroblastoma normally occurs inside and around the adrenal glands, that have related origins to nerve cells and sit on top of the kidneys. But, neuroblastoma can also occur in other parts of the abdomen and in the chest, pelvis and neck, any areas where groups of nerve cells exist.
Neuroblastoma frequently develops in children who are 5 years of age or younger, although it may not often occur in older children.
Some types of neuroblastoma disappear on their own, whereas some may need of several treatments. The preferences for child’s neuroblastoma treatment may depend on a number of factors.
What are the symptoms of neuroblastoma?
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma may depend on what area of the body is affected.
The signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma cancer in abdomen, which is the most frequent form are the following.
- Abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel habits like diarrhea
- Formation of mass under the skin that is not tender when touched
- Inflammation in the legs
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma in the chest may show the following.
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Changes to the eyes which includes the drooping of the eyelids and uneven size of the pupil
Other signs and symptoms are the following.
- Lumps of tissue underneath the skin
- Eyeballs that appear to protrude from the sockets
- Dark circles around the eyes, may be alike to bruises
- Back pain
- Fever
- Inexplicable weight loss
- Bone pain
What are the causes of neuroblastoma?
Neuroblastoma start in neuroblasts, an immature nerve cells wherein the fetus is a part of its growth development. As the fetus become full grown, neuroblasts finally turn into nerve cells and fibers and the cells that build the adrenal glands. Most of the neuroblasts are grown-up by birth, although research studies discover few of the immature neuroblasts in newly born babies. Majority of the cases, these neuroblasts mature and fade away. However, some neuroblasts form a tumor that lead to neuroblastoma.
The precise thing that causes the initial genetic mutation that result to neuroblastoma is not yet clear. Medial researchers consider the mutation takes place during pregnancy or soon after birth since neuroblastoma frequently affects very young children.
What are the complications of neuroblastoma?
Some of the complications of neuroblastoma may include the following.
- Neuroblastoma may reach or may spread to other areas of the body such as the bone marrow, lymph nodes, liver, skin and bones.
- Tumors may develop and may cause pressure on the spinal cord that may lead to compression. Spinal cord compression may cause pain and even paralysis.
- Neuroblastoma may produce certain chemicals that may cause irritation to other normal tissues that may lead to paraneoplastic syndromes. Signs and symptoms of paraneoplastic syndromes that develop rarely in people affected with neuroblastoma are the rapid eye movements and trouble with coordination. Other unusual causes of paraneoplastic syndrome are diarrhea and abdominal swelling.
What are the treatments for neuroblastoma?
Doctor may consider a lot of factors in making treatment plan. Factors may include the child’s age, the type of cells involved in the cancer, stage of the cancer, and if there are any irregularities in the chromosomes and genes. All these information may help the doctor of what treatment or combination of treatments that may give to the person affected with neuroblastoma. Treatments for neuroblastoma may include the following.
1.    Surgical procedure.
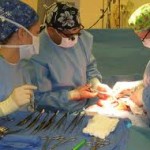 Doctor can make use of surgical procedure in removing cancer cells to children affected with low-risk neuroblastoma. But still depends on the site and size of the tumor if it can be entirely removed. Tumors that are located to nearby vital organs such as the spinal cord or the lungs may be too dangerous to remove. In this case, other treatments like radiation and chemotherapy may be used to destroy the remaining the cells.
Doctor can make use of surgical procedure in removing cancer cells to children affected with low-risk neuroblastoma. But still depends on the site and size of the tumor if it can be entirely removed. Tumors that are located to nearby vital organs such as the spinal cord or the lungs may be too dangerous to remove. In this case, other treatments like radiation and chemotherapy may be used to destroy the remaining the cells.
2.    Chemotherapy
 Chemotherapy makes use of chemicals to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy aims to destroy the fast growing cells in the body including the cancer cells. Sadly to say, chemotherapy also destroys the healthy cells that grow rapidly like the cells in the hair follicles and in the gastrointestinal system that can cause side effects. Chemotherapy is most helpful in children affected with low-risk neuroblastoma wherein the tumor can no be removed through surgery. Combination of chemotherapy drugs are often applied to children affected with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma. High doses of chemotherapy medicines are more often given to children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
Chemotherapy makes use of chemicals to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy aims to destroy the fast growing cells in the body including the cancer cells. Sadly to say, chemotherapy also destroys the healthy cells that grow rapidly like the cells in the hair follicles and in the gastrointestinal system that can cause side effects. Chemotherapy is most helpful in children affected with low-risk neuroblastoma wherein the tumor can no be removed through surgery. Combination of chemotherapy drugs are often applied to children affected with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma. High doses of chemotherapy medicines are more often given to children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
3.    Radiation therapy
 Radiation therapy makes use of high doses of energy particles to damage the cancer cells. Radiation therapy mostly affects the part where it is intended. Side effects of radiation therapy may depend on the location where the radiation is being directed and the quantity being administered.
Radiation therapy makes use of high doses of energy particles to damage the cancer cells. Radiation therapy mostly affects the part where it is intended. Side effects of radiation therapy may depend on the location where the radiation is being directed and the quantity being administered.
4.    Stem cell transplant
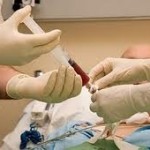 Stem cell transplant may be given to children affected with high-risk neuroblastoma using their own blood stem cells. The bone marrow creates stem cells that mature and develop into white and red cells and platelets that construct blood. The child might go through a process of filtering and collecting the stem cells from his or her blood. The child’s stem cells will then going to inject into the child’s body wherein they can make new and healthy blood cells.
Stem cell transplant may be given to children affected with high-risk neuroblastoma using their own blood stem cells. The bone marrow creates stem cells that mature and develop into white and red cells and platelets that construct blood. The child might go through a process of filtering and collecting the stem cells from his or her blood. The child’s stem cells will then going to inject into the child’s body wherein they can make new and healthy blood cells.
Do not hesitate to ask your doctor of what effective treatment plan may be helpful to the present condition your child
