Cardiovascular diseases are one of the most common problems and causes of death worldwide. This encompasses the diseases of the heart and blood vessels. This is brought about by poor diet and unhealthy lifestyle. When the heart and the blood vessels are suffering, then the rest of the body systems are affected. This leads to much more organ system failures that might very well cause the patient’s death.
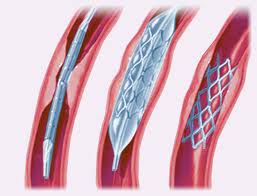
One of the most effective means of dealing with cardiovascular diseases is by undergoing an angioplasty procedure. An angioplasty procedure is a form of surgery that repairs diseased or very damaged arteries or veins. It can be performed on a particular blood vessel outside the heart or inside the heart. The angioplasty procedure performed inside the heart is called coronary angioplasty. Generally, this surgical procedure uses a balloon catheter to open up the arteries that are blocked. It is often inserted from a large artery that is usually in the groin area, and then pushed towards the affected blood vessel. This allows the blood flow to be improved. If you do not want to undergo a bypass or an open heart surgery, then this is a great alternative. Here are some of the things that you have to know about angioplasty procedure that you might just want to discuss with your doctor:
1. Goals
 The goals of angioplasty procedure are to eliminate the chest pain (angina) and to lessen the damage to the heart muscles. Angina is a symptom that involves pain in the chest area. This is brought about by the reduced flow of blood that results to less oxygenation. If the tissues are not well-oxygenated, pain ensues. Damage to the cardiac muscles happens when there are ischemic tissues already. If the blood flow is completely blocked, there is a high probability of damage or even necrosis.
The goals of angioplasty procedure are to eliminate the chest pain (angina) and to lessen the damage to the heart muscles. Angina is a symptom that involves pain in the chest area. This is brought about by the reduced flow of blood that results to less oxygenation. If the tissues are not well-oxygenated, pain ensues. Damage to the cardiac muscles happens when there are ischemic tissues already. If the blood flow is completely blocked, there is a high probability of damage or even necrosis.
2. Improvements
 Through the years, there have been large improvements to the angioplasty procedure already. Nowadays, stents, lasers, and plaque removers are already used. Stents are very small meshed tubes that look like springs. These are the ones inserted into the blood vessels. Medication is coated onto these stents to prevent the blood vessel from constricting and closing again. If a stent is used, there is lesser probability that the patient’s blood vessels will close up again after the initial six months. Lasers are used to dissolve the plaque that formed inside of the arteries. Plaque removers cut out the plaque that makes the blood vessels narrow.
Through the years, there have been large improvements to the angioplasty procedure already. Nowadays, stents, lasers, and plaque removers are already used. Stents are very small meshed tubes that look like springs. These are the ones inserted into the blood vessels. Medication is coated onto these stents to prevent the blood vessel from constricting and closing again. If a stent is used, there is lesser probability that the patient’s blood vessels will close up again after the initial six months. Lasers are used to dissolve the plaque that formed inside of the arteries. Plaque removers cut out the plaque that makes the blood vessels narrow.
3. Factors to consider
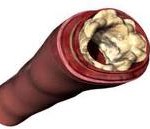 Doctors consider the number of blocked arteries, where these arteries are located, how severe they are, other underlying procedures that you may have and of course, your preference, before they recommend an angioplasty procedure over a bypass surgery. If your blood vessel blockage is small, if the blockage could be reached by an angioplasty tube, if the affected artery is not a main blood vessel that supplies the left side of the heart, and if you have not had a history of heart failure yet, an angioplasty procedure is recommended.
Doctors consider the number of blocked arteries, where these arteries are located, how severe they are, other underlying procedures that you may have and of course, your preference, before they recommend an angioplasty procedure over a bypass surgery. If your blood vessel blockage is small, if the blockage could be reached by an angioplasty tube, if the affected artery is not a main blood vessel that supplies the left side of the heart, and if you have not had a history of heart failure yet, an angioplasty procedure is recommended.
4. Advantages
 It is advantageous for you to undergo an angioplasty procedure because technically, it is not a surgery. It is also used with a mild sedative (local anesthetic), so you won’t feel any pain upon insertion of the tube. An angioplasty procedure also has a shorter period of recovery than bypass surgery. This also has the same status of survival as when you undergo a bypass surgery.
It is advantageous for you to undergo an angioplasty procedure because technically, it is not a surgery. It is also used with a mild sedative (local anesthetic), so you won’t feel any pain upon insertion of the tube. An angioplasty procedure also has a shorter period of recovery than bypass surgery. This also has the same status of survival as when you undergo a bypass surgery.
5. Risks
 Some risks of an angioplasty procedure are bleeding from the target blood vessel, damage sustained by the target blood vessel, secondary infection, allergic reaction from the procedure, possible heart attack, occurrence of stroke, need for an immediate open-heart surgery after, and death.
Some risks of an angioplasty procedure are bleeding from the target blood vessel, damage sustained by the target blood vessel, secondary infection, allergic reaction from the procedure, possible heart attack, occurrence of stroke, need for an immediate open-heart surgery after, and death.
6. Recovery
 Here are some tips when you recover from an angioplasty procedure: if you had the tube inserted into your groin, lie flat; if you had the tube inserted into your arm, do not lie flat; pressure should be applied on the area where the tube was inserted, then lie still until the blood vessel closes; and have an assisted walking session. During recovery time, the attending healthcare provider will regularly check your blood pressure, heart rate, and bleeding in the area of insertion. You will experience a week of soreness on the particular affected area. But you may be discharged one to two days after the angioplasty procedure. When you go home, you will have instructions on the medications you have to take (anticoagulants, antiplatelets {Plavix, Aspirin}), what exercises you should perform, the follow up schedules with your doctor, assessing signs and symptoms of infection (inflammation, redness, drainage), assessing pain and bleeding, and chest pain.
Here are some tips when you recover from an angioplasty procedure: if you had the tube inserted into your groin, lie flat; if you had the tube inserted into your arm, do not lie flat; pressure should be applied on the area where the tube was inserted, then lie still until the blood vessel closes; and have an assisted walking session. During recovery time, the attending healthcare provider will regularly check your blood pressure, heart rate, and bleeding in the area of insertion. You will experience a week of soreness on the particular affected area. But you may be discharged one to two days after the angioplasty procedure. When you go home, you will have instructions on the medications you have to take (anticoagulants, antiplatelets {Plavix, Aspirin}), what exercises you should perform, the follow up schedules with your doctor, assessing signs and symptoms of infection (inflammation, redness, drainage), assessing pain and bleeding, and chest pain.
You should remember that women, diabetics, and people 75 years old and older have higher risks in experiencing complications in undergoing an angioplasty procedure. So you really have to coordinate with your doctor.