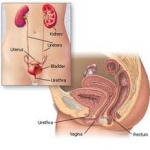
Bladder pain can result from inflammation, infection, damage or injury to the bladder. The symptoms may be constant or variable and may improve or worsen with movement. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, stabbing, burning or throbbing and can range in intensity from mild to severe.
Bladder Problems Spotlight
There are many potential causes of bladder pain. Urinary tract infection and interstitial cystitis are among the most common. Interstitial cystitis is a bladder function abnormality that is related to the central nervous system’s ability to regulate the bladder. It causes bladder pain that may also be accompanied by pain in the genitals, pelvis and anal region. Urinary tract infection is a cause of bladder pain that is typically accompanied by pain with urination, increased urinary frequency, or urgency (pressing need to urinate).
In other cases, bladder pain may come from a chronic underlying disease, such as cancer, endometriosis, and bowel disorders. Malignant tumors can cause bladder pain, as well as pain with urination, abdominal pain, and bloody urine. Bladder scarring or damage to adjoining structures, such as the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, may also contribute to bladder pain. If the urethra is constricted (a urethral stricture), urine may remain in the bladder, leading to pain and infection.
The duration and course of bladder pain vary widely depending on the cause. Bladder pain may be present constantly, sporadically, or only when the bladder is full.
Bladder pain may be associated with a serious condition. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you experience the following symptoms: high fever (higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit), the inability to urinate, or severe abdominal pain.
If you have difficulty urinating, notice blood in your urine, or if your bladder pain is persistent or causes you concern, seek prompt medical care.
What causes bladder pain?
Bladder pain may be the result of multiple factors, including infection, disease or injury to the bladder. Symptoms may arise if you experience problems with normal bladder function, such as difficulty urinating, increased frequency of urination, or painful urination.
Bladder pain can involve other regions of the body if it is caused by cancers, endometriosis, or bowel disorders. These conditions can lead to bladder damage, and their symptoms may include bloody urine, fever, or pain in the lower back, abdomen or side.
Urinary disorders that cause bladder pain
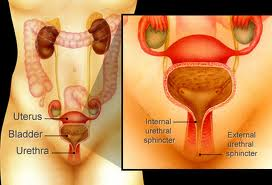 Bladder pain may be caused by urinary disorders including:
Bladder pain may be caused by urinary disorders including:
- Benign or malignant tumors
- Congenital abnormality
- Injury
- Interstitial cystitis
- Kidney infection
- Urethral stricture
- Urinary tract infection
Cystitis
One of the most common causes of bladder pain is cystitis (bladder infection). The bladder becomes inflamed and irritated due to trapped bacteria inside the urethra and bladder.
Besides bladder pain, other common symptoms associated with cystitis include difficulty urinating, frequent urination, dark urine (sometimes bloody urine), backaches and low-grade fever. If left untreated, cystitis could move into the kidneys and cause a kidney infection.
Cystitis needs to be diagnosed by a medical doctor and treated with antibiotics. Drinking a lot of water can help flush out harmful bacteria and alleviate symptoms.
Urethral Stricture
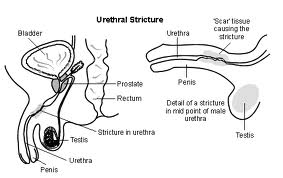 Urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra (the tube through which urine passes out of the body). This stricture is associated with bladder pain because the abnormal narrowing doesn’t allow all urine to be emptied from the bladder. This condition is more common in men than women.
Urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra (the tube through which urine passes out of the body). This stricture is associated with bladder pain because the abnormal narrowing doesn’t allow all urine to be emptied from the bladder. This condition is more common in men than women.
Some symptoms related to urethral stricture are burning sensations during urination, reduction in urine flow and frequent urgency to urinate. Because semen passes through the urethra, men sometimes experience painful ejaculations.
Depending upon the severity of the condition, doctors prescribe either antibiotics or surgery.
Other causes of bladder pain
Bladder pain can also be caused by other causes including:
- Bowel disorders
- Endometriosis
Serious or life-threatening causes of bladder pain
In some cases, bladder pain may be a symptom of a serious or life-threatening condition that should be immediately evaluated. These include cancers of the bladder or surrounding organs.
Questions for diagnosing the cause of bladder pain
 To diagnose your condition, your doctor or licensed health care practitioner will ask you several questions related to your bladder pain including:
To diagnose your condition, your doctor or licensed health care practitioner will ask you several questions related to your bladder pain including:
- When did you first notice your bladder pain?
- When do you feel bladder pain?
- Do you have any other symptoms?
- What medications are you taking?
What are the potential complications of bladder pain?
The potential complications of bladder pain depend on their cause. Bladder pain that is associated with a serious medical condition, such as cancer, may have long-term and even life-threatening complications. Further, bladder pain that is associated with an acute bladder infection could lead to a more serious complication, such as widespread infection.
Once the underlying cause is diagnosed, it is important for you to follow the treatment plan that you and your health care professional design specifically for you to reduce the risk of potential complications. Left untreated, conditions that cause bladder pain could lead to the following complications:
- Organ failure or dysfunction
- Permanent or chronic pain
- Sepsis (life-threatening bacterial blood infection)
- Spread of cancer