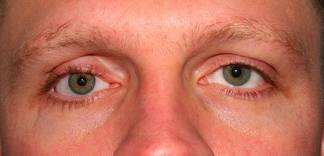
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your health care provider will get a medical history and perform a physical examination.
Medical history questions may include:
- Are both eyelids affected or just one?
- How long has this been present?
- Is it getting worse or staying the same?
- Is it present all of the time or only sometimes?
- What other symptoms do you have?
The physical examination may include a detailed assessment of nerve functioning.
Diagnostic tests that may be performed include:
- Slit-lamp examination
- Tensilon test
Slit-lamp exam
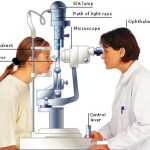 The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
The slit-lamp is a low-power microscope combined with a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine in a thin beam.
You will sit in a chair with the instrument placed in front of you. You will be asked to rest your chin and forehead on a support to keep your head steady.
The health care provider will examine your eyes, especially the eyelids, cornea, conjunctiva, sclera, and iris. Often a yellow dye (fluorescein) is used to help examine the cornea and tear layer. The dye is either added as a drop, or the health care provider may touch a fine strip of paper stained with the dye to the white of your eye. The dye rinses out of the eye with tears as you blink.
Next, drops may be placed in your eyes to widen (dilate) your pupils. The drops take about 15 to 20 minutes to work. The slit-lamp examination is then repeated using another small lens held close to the eye, so the back of the eye can be examined.
Pathology
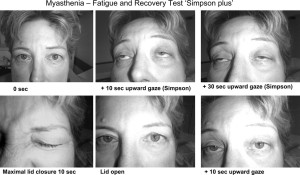 Myasthenia gravis is a common neurogenic ptosis which could be also classified as neuromuscular ptosis because the site of pathology is at the neuromuscular junction. Studies have shown that up to 70% of myasthenia gravis patients present with ptosis, and 90% of these patients will eventually develop ptosis. In this case, ptosis can be unilateral or bilateral and its severity tends to be oscillating during the day, because of factors such as fatigue or drug effect. This particular type of ptosis is distinguished from the others with the help of a Tensilon challenge test and blood tests. Also, specific to myasthenia gravis is the fact that coldness inhibits the activity of cholinesterase, which makes possible differentiating this type of ptosis by applying ice onto the eyelids. Patients with myasthenic ptosis are very likely to still experience a variation of the drooping of the eyelid at different hours of the day.
Myasthenia gravis is a common neurogenic ptosis which could be also classified as neuromuscular ptosis because the site of pathology is at the neuromuscular junction. Studies have shown that up to 70% of myasthenia gravis patients present with ptosis, and 90% of these patients will eventually develop ptosis. In this case, ptosis can be unilateral or bilateral and its severity tends to be oscillating during the day, because of factors such as fatigue or drug effect. This particular type of ptosis is distinguished from the others with the help of a Tensilon challenge test and blood tests. Also, specific to myasthenia gravis is the fact that coldness inhibits the activity of cholinesterase, which makes possible differentiating this type of ptosis by applying ice onto the eyelids. Patients with myasthenic ptosis are very likely to still experience a variation of the drooping of the eyelid at different hours of the day.
The ptosis caused by the oculomotor palsy can be unilateral or bilateral, as the subnucleus to the levator muscle is a shared, midline structure in the brainstem. In cases in which the palsy is caused by the compression of the nerve by a tumor or aneurysm, it is highly likely to result into an abnormal ipsilateral papillary response and a larger pupil. Surgical third nerve palsy is characterized by a sudden onset of unilateral ptosis and an enlarged or sluggish pupil to the light. In this case, imaging tests such as CTs or MRIs should be considered. Medical third nerve palsy, contrary to surgical third nerve palsy, usually does not affect the pupil and it tends to slowly improve in several weeks. Surgery to correct ptosis due to medical third nerve palsy is normally considered only if the improvement of ptosis and ocular motility are unsatisfactory after half a year. Patients with third nerve palsy tend to have diminished or absent function of the levator.
When caused by Horner’s syndrome, ptosis is usually accompanied by miosis and anhidrosis. In this case, the ptosis is due to the result of interruption innervations to the sympathetic, autonomic Muller’s muscle rather than the somatic levator palpebrae superioris muscle. The lid position and pupil size are typically affected by this condition and the ptosis is generally mild, no more than 2 mm. The pupil might be smaller on the affected side. While 4% cocaine instilled to the eyes can confirm the diagnosis of Horner’s syndrome, Hydroxyamphetamine eye drops can differentiate the location of the lesion.
Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia is a systemic condition that occurs suddenly and which usually affects only the lid position and the external eye movement, without involving the movement of the pupil. This condition accounts for nearly 45% of myogenic ptosis cases. Most patients develop ptosis due to this disease in their adulthood. Characteristic to ptosis caused by this condition is the fact that the protective up rolling of the eyeball when the eyelids are closed is very poor.
Treatment
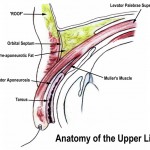 Aponeurotic and congenital ptosis may require surgical correction if severe enough to interfere with vision or if cosmesis is a concern. Treatment depends on the type of ptosis and is usually performed by an ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgeon, specializing in diseases and problems of the eyelid.
Aponeurotic and congenital ptosis may require surgical correction if severe enough to interfere with vision or if cosmesis is a concern. Treatment depends on the type of ptosis and is usually performed by an ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgeon, specializing in diseases and problems of the eyelid.
Surgical procedures include:
- Levator resection
- Müller muscle resection
- Frontalis sling operation
Non-surgical modalities like the use of “crutch” glasses or special Scleral contact lenses to support the eyelid may also be used.
Ptosis that is caused by a disease will improve if the disease is treated successfully.