Testicular cancer develops in the testicles or testes, which to be found in the scrotum, a loose bag of skin under the penis. The testicles are the one responsible in producing sperm and male sex hormones for reproduction. Testicular cancer is a type of cancer that considered being uncommon. However, testicular cancer is the most frequent cancer that affects American males that occurs in between the ages of 15 and 34.
Testicular cancer may have several treatments that may depend on the type and stage of it. Testicular cancer is very much treatable even if the cancer already reaches beyond the testicle. It is important to have a regular testicular self-examination to detect early development and the possibility for favorable treatment great.
What are the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer?
Testicular cancer usually affects only one testicle. Signs and symptoms of testicular cancer are the following.
- Enlargement or presence of lump in either testicle
- Dull pain in the groin or abdomen
- Feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- A rapid collection of liquid in the scrotum
- Pain or soreness in the scrotum or the testicle
- Tenderness or swelling of the breasts
What are the causes of testicular cancer?
It is not yet understandable of what really causes testicular cancer. Health care providers know that testicular cancer develops when the healthy cells in a testicle changed. Normally, healthy cells develop and divide in a systematic way to maintain the body functioning generally. However, in unknown reason some cells grow abnormally resulting to cancer cells. These cancer cells will keep on dividing even when new cells are not needed.  These accumulating cells develop a mass in the testicle. Almost all testicular cancer starts in the germ cells. Germ cells are cells in the testicles responsible in producing immature sperm. The reason why germ cells turn out to be abnormal and become cancer is not yet known.
What is the risk factors affecting testicular cancer?
There are factors that may increase the possibility of having testicular cancer they are the following.
- Men whose testicle never descended during their fetal development have a greater possibility of having testicular cancer than to those men who have testicle that descended normally. Even if the testicle has been transferred through surgical procedure to the scrotum, still the risk of developing testicular cancer remains.
- Irregular development of testicle like Klinefelter’s syndrome may have greater possibility of having testicular cancer.
- If testicular cancer runs in the family, you may also have greater possibility of developing testicular cancer.
- Testicular cancer mostly affects men whose ages are between 15 and 34. But it can develop at any age.
- Testicular cancer mostly affects white men than black men.
What are the treatments for testicular cancer?
There are choices in treating testicular cancer which varies on the stage and type of testicular cancer, your preferences and your health generally. Treatments for testicular cancer may include the following.
1.    Surgical procedure.
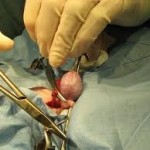 Removing the testicle through surgical procedure is the main treatment for almost types and stages of testicular cancer. There will have anesthetics during the surgical procedure. The procedure will be done by making incision in the groin then extracts the whole testicle through the opening. If you prefer, a prosthetic, saline-filled testicle can be inserted. Removing lymph nodes in the groin can also be done through surgical procedure. Making large incision in your abdomen is the way to remove the lymph nodes. Surgical procedure may be the only treatment needed in the early stage of testicular cancer.
Removing the testicle through surgical procedure is the main treatment for almost types and stages of testicular cancer. There will have anesthetics during the surgical procedure. The procedure will be done by making incision in the groin then extracts the whole testicle through the opening. If you prefer, a prosthetic, saline-filled testicle can be inserted. Removing lymph nodes in the groin can also be done through surgical procedure. Making large incision in your abdomen is the way to remove the lymph nodes. Surgical procedure may be the only treatment needed in the early stage of testicular cancer.
2.    Radiation therapy.
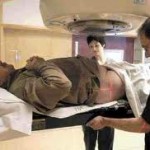 Radiation therapy is the choice treatment that is often used in men who have the seminoma kind of testicular cancer. But radiation therapy can also be used in certain situations in men who have nonseminoma kind of testicular cancer. This therapy makes use of high-powered energy beams like x-rays to kill the cancer cells. Radiation therapy may have side effects like fatigue, skin redness and irritation in your groin and abdominal parts.
Radiation therapy is the choice treatment that is often used in men who have the seminoma kind of testicular cancer. But radiation therapy can also be used in certain situations in men who have nonseminoma kind of testicular cancer. This therapy makes use of high-powered energy beams like x-rays to kill the cancer cells. Radiation therapy may have side effects like fatigue, skin redness and irritation in your groin and abdominal parts.
3.    Chemotherapy.
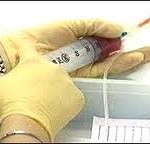 Chemotherapy treatment makes use of drugs to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy frequently recommended by the doctor after having surgical procedure. This can also be used before or after removal of the lymph node. There are different side effects of chemotherapy drug depending on what being use. The frequent side effects are nausea, fatigue, infertility, hair loss and increased possibility of having infection. However, there are treatments and medications available that may help to lessen a number of the side effects of chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy treatment makes use of drugs to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy frequently recommended by the doctor after having surgical procedure. This can also be used before or after removal of the lymph node. There are different side effects of chemotherapy drug depending on what being use. The frequent side effects are nausea, fatigue, infertility, hair loss and increased possibility of having infection. However, there are treatments and medications available that may help to lessen a number of the side effects of chemotherapy.
Regular testicular self-examination can be very helpful in early detection of testicular cancer. Consult your doctor immediately if you observed any changes to the part or area of the body being concerned.
