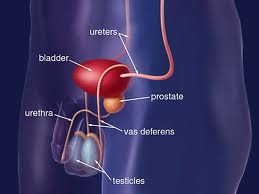
Bladder cancer is the type of cancer that starts in the bladder, an organ that can be found in the pelvic part that holds urine. Bladder cancer usually starts in the cells that line within the bladder. Bladder cancer can take place at any age, although it normally affects older adults.
Bladder cancers are often detected at an early phase wherein it is greatly treatable. But even the early stage of bladder cancer has still the possibility to come again. This is the reason why bladder cancer survivors have frequently to go through follow-up test to check if bladder cancer recurs after treatment.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Symptoms of the bladder cancer may include the following.
- Presence of blood in the urine or called hematuria. Urine may come out as dark yellow, cola colored or bright red; or the urine may appear normal but upon viewing in a microscopic examination there is the presence of blood.
- Frequent urination
- Urinary tract infection
- Painful urination
- Pain in the abdominal area
- Back pain
What is the risk factors affecting bladder cancer?
The exact reason of what causing bladder cancer is not yet clear. However the factors that may increase the possibility of having bladder cancer are being identified by the doctors and these are the following.
- The risk of developing bladder cancer is greater as people get older. Bladder cancer can develop at any age but it is seldom found in people with an age of less than 40.
- White races have greater possibility of having bladder cancer than with other races.
- Men have greater risk of having bladder cancer than women.
- Smoking may tend to increase the risk of developing bladder cancer by causing harmful chemicals to build up in the urine. The body will processes the harmful chemicals present in the smoke and excretes some of them in the urine. These chemicals may tend to harm the lining of the bladder that will increase the possibility of having bladder cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals like arsenic and chemicals being used in the manufacture of rubber, dyes, leather, textiles and pain products have greater possibility of having bladder cancer. People who smoke and are also exposed to toxic chemicals may even have greater possibility of developing bladder cancer.
- Cancer survivor who had taken anti-cancer drug cyclophosphamide increases the possibility of developing bladder cancer. People who had undergone radiation treatments intended at the pelvis area for a previous cancer may have an increased risk of having developing cancer.
- Chronic inflammation of the bladder or frequent urinary infections may enhance the risk of developing bladder cancer. Long-term use of urinary catheter may also tend to increase the risk of having squamous cell bladder cancer.
- If there is one or more of your immediate relatives have a history of bladder cancer, there is a greater possibility for you to develop the disease. If you’ve had bladder cancer, there is still the greater possibility of having it again.
What are the treatments for bladder cancer?
The treatments for bladder cancer may depend on the stage of bladder cancer, your overall health and   your treatment choices. Some of the treatments may include the following.
1.    Surgery.
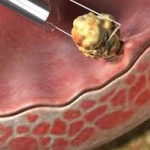 If the cancer is on the early stage and very small, the doctor may recommend the transurethral resection of bladder tumor or TURBT wherein the bladder cancer that are enclosed to the inner layers of the bladder are being removed. This procedure is being done by passing a small wire loop through the urethra and going into the bladder. The loop has an electric current that used to burn away the cancer cells. This TURBT procedure may cause bloody or painful urination for a few days after going through it.
If the cancer is on the early stage and very small, the doctor may recommend the transurethral resection of bladder tumor or TURBT wherein the bladder cancer that are enclosed to the inner layers of the bladder are being removed. This procedure is being done by passing a small wire loop through the urethra and going into the bladder. The loop has an electric current that used to burn away the cancer cells. This TURBT procedure may cause bloody or painful urination for a few days after going through it.
There are many ways of surgery in removing the cancer cells in the bladder. Another one is the segmental cystectomy or sometimes called partial cystectomy that only the part of the bladder that have cancer cells are being remove. This surgical procedure may be a choice if the cancer is limited only to one part of the bladder that can simply be removed without damaging the function of the bladder.
 2.    Biological therapy or immunotherapy
 Biological therapy or sometimes called immunotherapy, works by giving signal to the body’s immune system helping to fight the cancer cells. This biological therapy for bladder cancer is normally administered all the way through the urethra and directly in the bladder.
Biological therapy or sometimes called immunotherapy, works by giving signal to the body’s immune system helping to fight the cancer cells. This biological therapy for bladder cancer is normally administered all the way through the urethra and directly in the bladder.
3.    Chemotherapy
 Chemotherapy makes use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. There are two or more medicines that are used in combination in using chemotherapy treatment in bladder cancer. The medications used can be administered intravenously or through intravesical therapy wherein the medicines are being administered directly to the bladder by passing a tube through the urethra. Chemotherapy treatment can be used before or after surgical operation.
Chemotherapy makes use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. There are two or more medicines that are used in combination in using chemotherapy treatment in bladder cancer. The medications used can be administered intravenously or through intravesical therapy wherein the medicines are being administered directly to the bladder by passing a tube through the urethra. Chemotherapy treatment can be used before or after surgical operation.
4.    Radiation therapy
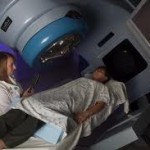 Radiation therapy makes use of high-energy beams intended on the part of the cancer to kill the cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be an external beam radiation, it comes from a machine outside the body or brachytherapy that uses device that are being placed inside the bladder.
Radiation therapy makes use of high-energy beams intended on the part of the cancer to kill the cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be an external beam radiation, it comes from a machine outside the body or brachytherapy that uses device that are being placed inside the bladder.
These are all the treatments can be used in destroying the cancer cells causing bladder cancer. Consult your doctor of what treatment you prefer to obtain a successful action in dealing with this disorder.