Our blood sugar plays the role of fuel in order for us to do our activities of daily living. The brain also functions and needs a good supply of sugar in the blood in order for it to work. The term hypoglycemia refers to the clinical syndrome that result from low blood sugar.  Symptoms may vary from one person to another. A lot of people think that a high blood sugar is dangerous but neglects the idea that a low blood sugar can also be dangerous and may lead to other complications such as shock. A hypoglycemic shock may also lead to death. A lot of people have undiagnosed hypoglycemia. Knowledge is always the key in any aspect. Learning the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia will actually help in the monitoring of blood sugar in people with or without diabetes and will prevent the effects and complications of low blood sugar.
Symptoms may vary from one person to another. A lot of people think that a high blood sugar is dangerous but neglects the idea that a low blood sugar can also be dangerous and may lead to other complications such as shock. A hypoglycemic shock may also lead to death. A lot of people have undiagnosed hypoglycemia. Knowledge is always the key in any aspect. Learning the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia will actually help in the monitoring of blood sugar in people with or without diabetes and will prevent the effects and complications of low blood sugar.
How blood sugar level is obtained?

Insulin therapy always needs blood sugar monitoring for safety and for evaluation of effectiveness of therapy
Symptoms of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar should always be watched out for. Any deviation form the normal range of blood sugar level can be culprits of many physiological and psychological symptoms. The symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe, and may vary from person to person, which is the very reason why critical assessment should be done at all times. A decrease in blood sugar level can happen slowly, intermittently, or very rapid that it could cause serious medical conditions. Hypoglycemic symptoms can also mimic other medical conditions. Coupled with symptom checking, monitoring of the blood sugar level is a must.

Color Palette Reference
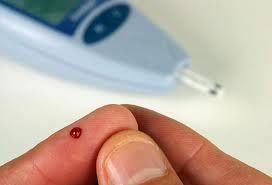
Blood sugar test is a way to get the numerical concentration of sugar or glucose in the blood. The basic blood sugar monitoring test is done with a needle prick to be able to get a minimal amount of blood needed, which is usually a drop of blood. This is done using lancets or a puncture device to aseptically draw a drop of blood. The fingers of the hands are the usual sites for blood specimen extraction. The lateral sides of the tip of the finger are the best sites because few pain nerves lie on that area, to decrease the level of pain of the person, most especially if the person is under a frequent blood sugar. Blood is dropped on a hemoglucotest strip. This is usually done prior to feeding. Reading and interpretation of results vary from brands and manufacturers. It is always integral to read the instructions before using a test strip or device. New technologies offer electronic meter devices for measuring blood sugar. Blood is drawn from a prick and then dropped to a testing strip that is automatically read in a few seconds. These devices are portable and are user-friendly for home and hospital use.
Some doctors may request for a continuous glucose monitoring test. This is done using a disposable sensor that is placed under the skin that is worn for a few days for continuous monitoring. This type of test is done for those requiring very frequent blood glucose monitoring, especially indicated for those who have fluctuating blood glucose levels. Continuous monitoring of blood sugar is done to evaluate effectiveness of insulin therapy and to monitor changes of blood sugar during activities such as feeding, exercise, etc.
Normal Values of Blood Sugar
The normal blood sugar level ranges from 3.6 to 5.8 mmol/L or 64.8 to 104.4 mh/dL. Any deviation from the normal values can produce symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Symptoms of low blood sugar if untreated can be life threatening in severe cases. These are the symptoms to look out for in order to immediately treat and prevent complications:
Sweating, cold clammy hands and feet, shaking between meals, crankiness, confusion, inability to concentrate, weakness, fatigability, tingling sensations, nervousness, pounding or racing heart, glassy eyes, feelings of uneasiness, speech difficulties, fuzzy head, migraines, mood swings, faintness, nausea, vomiting, feelings of depression, melancholia, obsessive-compulsive behavior, slurred speech, poor coordination, disorientation, alteration in attention, agitation, unresponsiveness, changes in sensorium, convulsions, unconsciousness, etc.
Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Treatment of hypoglycemia requires critical blood glucose monitoring and restoring of blood glucose levels to normal range. A very rapid increase in blood sugar levels may also have dangerous effects. This is done in precaution because it widely affects the person’s sensorium, physical and mental health. To treat hypoglycemia, it is always best to eat foods that take a while to be digested so that there will not be a very rapid raise in the blood sugar levels. Reading the product labels and nutrition facts can greatly help in monitoring your caloric intake. A well balanced diet is always imperative and including foods such as eggs, meat, yoghurt, beans, nuts, protein rich foods and complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fresh vegetables, and fresh whole fruits are good examples of healthy carbohydrate rich foods that has sugar content that does not break down easily to simple sugars.