A pathogen is a microorganism that causes a disease. An opportunistic pathogen is one that exists harmlessly as part of the normal flora of the human body and does not become a threat until the body’s immune system fails or is disturbed. Candida albicans is considered an opportunistic pathogen.
Definition
Cadidiasis, also known as Moniliasis is a yeast infection that results from the overgrowth of fungal yeast anywhere in the body. This is caused by strains of Candida. Candida albicans is a strain that accounts for most cases but other strains, such as Candida glabrata, may also be implicated. Many women with healthy vaginal ecosystems harbor this type of yeast but are asymptomatic. These fungi are found in many parts of the body as normal flora but under certain conditions, they become cultured and grow rapidly that can cause an infection and produce symptoms. Candidiasis is the most common type of yeast infection that can occur in many parts of the body—the oral mucosa, periunal, inguinal, intergdigital, axillary, nail folds, nail beds, and genitor-urinary tract. The most areas that are affected are called the intertriginous areas.  Intertriginous areas are two skin parts that may often touch or rub together. The warmth and moisture and maceration of the skin permit the organisms to thrive.
Our skin has normal floras that provide protection to our skin. The sweat our glands produce also has a bactericidal effect for added protection but when all else fails, such as in a skin that is cut, bacteria is ready to enter since the skin barrier is damaged and infection is there to occur when immune and other defenses of the body also fail.
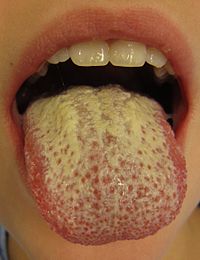
 Oral candidiasis is also called oral thrush. Popular sign of this infection are thick, white lacy patches on the top of a red base of the tongue or palate. An oral thrush can make it very difficult for the sufferer to eat or drink. There is a high risk for malnutrition and dehydration on a person suffering oral thrush.
Oral candidiasis is also called oral thrush. Popular sign of this infection are thick, white lacy patches on the top of a red base of the tongue or palate. An oral thrush can make it very difficult for the sufferer to eat or drink. There is a high risk for malnutrition and dehydration on a person suffering oral thrush.
Vulvo-vaginal candidiasis is a funal or yeast infection caused by Candida albicans on the genitals. Signs and symptoms are inflammation of vaginal epithelium producing itching, reddish irritation. A white cottage cheese-like discharge clinging to the epithelium is a common sign. Symptoms are usually more severe just before the menstruation and are usually less responsive to treatment during pregnancy.
A person with severe type of candidiasis is often also tested for presence of HIV infection because candidiasis is a disease caused by opportunistic pathogen. When the immune system is down, this is the time that the infection is harbored. When the infection goes into the bloodstream, it can be a systemic candidiasis which can be difficult to cure. If the infection reaches the brain, mental symptoms may occur.
Diagnosis
Some physicians can diagnose a simple candidal infection even without the use of diagnostic laboratory tests. Physicians will look for the popular white, cheesy substance found in the oral or vaginal mucosa. Symptomatic therapy is administered with antibiotics. When symptoms get worse and when the results are not achieved, this is the time to use laboratory exams to know the extent and why it does not cure. For vaginal candidiasis, a full gynecological examination is done. A speculum is used to hold the vagina open and to be able to view the surrounding tissues. A potassium hydroxide swab test is done to see the presence of spores and pseudomycin. This will be cultured with Saboraud’s glucose agar. A positive test will show growth of creamy, grayish, moist colonies in a bout 4 days. Other diagnostics such as blood tests and urine exams are also done to see if the infection has extended to the blood stream or to the urinary tract. People who have catheters may have their catheters tested for presence of Candida albicans in the urinary tract. A CT Scan or MRI of the brain will determine any extent of the disease to the brain.

C. albicans growth on an agar culture
Treatment
For oral thrushes, antifungal gargles and swallows such as Nystatin are used to kill the fungi and maintain oral health. Women who are breastfeeding should be evaluated for breast moniliasis as oral thrush to babies are common infections for breastfeeding women. Antifungal lozenges such as Trochles are also available as over-the-counter remedies for oral thrush. Fluconazole (Diflucan) oral pills or topical antifungal cream are effective to clear out the infection.
For vaginal thrushes, A week-long therapy of topical antifungals such as Tioconazole, Miconazole, and Clotrimazole are applied to the genitourinary areas to treat the infection. More serious and systemic infections may require hospital treatment and intravenous antibiotics for faster and more effective treatment.
Â